University of Leeds
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Resolution
-
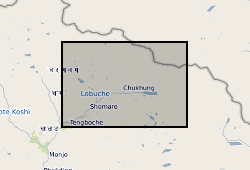
These data consist of a spreadsheet containing 557 ground control points (GCPs) collected in the Everest region of Nepal between October 2015 and October 2016. GCPs were collected using a Leica GS10 differential Global Positioning System (dGPS), post-processed against base station data at Syangboche. These final data have sub-centimetre accuracy (in x, y and z) in all cases. Point positions are heavily concentrated around meltwater ponds on the glacier surface, and prominent features around the glacier margin. These data will be used by PhD students and staff in the School of Geography, University of Leeds, to provide ground control for fine-resolution satellite imagery and Structure-from-Motion surveys to assess mass loss processes on Khumbu Glacier.
-
This data set contains example input and output files from density functional theory calculations of rare earth systems, using the Vienna Ab initio Simulation Package (VASP), The data set it split into two parts. The first data set contains the input and output files of molecular dynamics simulations of MCl3 in solution, where (M = Nd, Gd and Er) at ambient conditions, which was modelled at 341 K using the optB88 exchange-correlation functional. The calculations were run in order to investigate speciation in rare earth chloride solutions, including trends across the row, using a light (Nd), medium (Gd) and heavy (Er) rare earth. These particular calculations were used to validate classical interatomic potentials that were used to perform more complex simulation on larger systems and longer timescales. Only the first 2 ps of the trajectories are deposited here, since the complete trajectories are large. The second data set contains example input and output files for lattice dynamics calculations of the thermodynamics properties (heat capacity and entropy) of Nd-monazite and Nd-xenotime at ambient conditions up to 1200 K. In addition, it includes scripts for processing and plots of final results. These are useful for thermodynamical modelling of rare earth systems. Only the input and output files for Nd are deposited here, since the files are large and input files for Gd and Er are identical, save for the change in element.
-
These data files represent simulations of hydrated cation vacancies in the mantle mineral forsterite (Mg2SiO4) undertaken using the CASTEP atomic scale simulation code (http://www.castep.org/). Results from these simulations allow the structure relative stability of different defect configurations to be compared. Three types of cation vacancies are considered (M1, M2 and Si) each decorated by hydrogen in order to charge balance the system. For M1 and M2 this results in multiple configurations (with hydrogen bonded to different oxygen atoms around the vacant site). For Si there is only one configuration as all four oxygen atoms are bonded to hydrogen for the charge neutral defect. For each configuration input files detail the initial atomic structure of the defect along with simulation parameters. Output files record the progress of the simulation, the final atomic structure, the energy of this structure, and various predicted properties of the structure. Only ASCII output data is included as binary data created by CASTEP is not intended to be portable, and can easily be recreated using the ASCII files.
-
This data contains the results of student and professional perceptions surveys conducted in the UK before and after e-Learning training, as part of a project to determine the effectiveness of e-Learning as a training tool. The dataset include two surveys; before and after e-Learning training. Students and professionals were given two separate surveys which were combined to create one dataset. The surveys were collected between September 2015 and July 2018. The objective of the survey was to collect data on participants’ awareness, risk perceptions and self-reported behaviours on biosecurity for invasive species. The topics on both the before and after survey included age, role at institution, field of work/study, field activity environments, cleaning methods for equipment, outerwear/footwear and transport and awareness and perceptions of risk around invasive species and biosecurity campaigns. The data does not include the aggregated cleaning scores that were used for the analysis nor has it excluded any participants that were not used in the final data analysis. The dataset has been anonymised by removing names of respondents, email addresses, departments or organisations worked for or studied in, and text responses which could have made the participant identifiable. The research was funded by NERC project no NE/N008391/1. Full details about this nonGeographicDataset can be found at https://doi.org/10.5285/ac271791-b722-489c-9b68-b37316ec826c
-
The datasets contains species presence and background points, and their associated environmental data for non-native common wall lizard (Podarcis muralis). These data are included for local and national scale modelling of likelihood of species presence, as used in the modelling software MaxEnt. The .asc files included are the raw spatial data of parameters (i.e., distance to nearest road) used in modelling at various local regions, from which SWD 'samples with data' were extracted. Outputs from the local MaxEnt models produced the .txt files included. These serve as landscape layer inputs (habitat suitability and movement cost layers) for modelling population growth and spatial spread in the Individual based modelling platform, RangeShifter. Subsequent outputs of projected population growth (number of individuals per landscape cell) and x/y coordinates for each cell, are presented in files with the prefix Pop.csv and avg.csv (averaged data over 50 replicate runs). Full details about this dataset can be found at https://doi.org/10.5285/8ae3f9ef-9a75-4237-afbd-e01abe02e75b
-
The dataset provides transcripts from focus groups in Salima, Mangochi and Zomba (Malawi). The focus groups' discussions concern the monthly agricultural activities in association with the climate services and extreme weather events. The data were produced as part of NERC Program Science for Humanitarian Emergencies and Resilience (SHEAR). Grant reference - Improving Preparedness to Agro-Climatic Extremes in Malawi (IPACE-Malawi). Full details about this dataset can be found at https://doi.org/10.5285/2b8cb09f-9348-4115-a90e-818eade599af
-
The dataset provides transcripts from focus groups in Salima, Mangochi and Zomba (Malawi). The focus groups' discussions focused on important monthly agricultural activities in association with the climate services and extreme weather events. This outlined how climatic factors affected agricultural decision-making. The data were produced as part of NERC Program Science for Humanitarian Emergencies and Resilience (SHEAR). Grant reference - Improving Preparedness to Agro-Climatic Extremes in Malawi (IPACE-Malawi). Full details about this dataset can be found at https://doi.org/10.5285/199b0046-79a3-4e74-8152-17f10c376671
-

Excel file containing abundance data of planktonic foraminifer from IODP Expedition 375 Hole 1520C (41R-44R)
-
Data derived from UKCCSRC Call 2 Project C2-181. The journal article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.03.072. Sorption enhanced chemical looping steam reforming of methane (SE-CLSR) relies on the exothermicity of both a metal catalyst’s oxidation and the in situ CO2 capture by carbonation onto a solid sorbent to provide the heat demand of hydrogen (H2) production by steam reforming while generating a nearly pure H2 product. A brief thermodynamic analysis to study the main features of the SE-CLSR process is done prior to the reactor modelling work. Later, one dimensional mathematical model of SE-CLSR process in the packed bed configuration is developed using gPROMS model builder 4.1.0 under the adiabatic conditions. This model combines reduction of the NiO catalyst with the steam reforming reactions, followed by the oxidation of the Ni-based reduced catalyst. The individual models of NiO reduction, steam reforming with in situ CO2 capture on Ca-sorbent, and Ni re-oxidation are developed by using kinetic data available in literature and validated against previous published work. The model of SE-CLSR is then applied to simulate 10 alternative cycles of the fuel and air feed in the reactor. The performance of the model is studied in terms of CH4 conversion, CO2 capture efficiency, purity and yield of H2. The sensitivity of the process is studied under the various operating conditions of temperature, pressure, molar steam to carbon ratio (S/C) and mass flux of the gas phase. In this work, the operating conditions used for the production of H2 represent realistic industrial production conditions. The sensitivity analysis demonstrates that the developed model of SE-CLSR process has the flexibility to simulate a wide range of operating conditions of temperature, pressure, S/C and mass flux of the gas phase.
-
Dupont, Valerie (2016) Data for "Kinetics study and modelling of steam methane reforming process over a NiO/Al2O3 catalyst in an adiabatic packed bed reactor" in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. University of Leeds. Data file containing datasets used to generate the figures and tables in the paper. [Dataset] https://doi.org/10.5518/126. [Publication] http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.11.093
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service